Vaccination is a huge part of animal husbandry and ensuring you optimise flock production. Consider a pre-lamb vaccination for clostridial diseases, vaccinate with Toxovax (once) and Campylovexin (twice) prior to mating. Give iodine and/or selenium supplements if environmental conditions require it and a pre-lamb anthelmintic if faecal egg counts are high.
The clostridial diseases include pulpy kidney, tetanus, malignant oedema, black disease and black Leg. They are in the environment, they are the bugs responsible for decomposing dead organic matter either animal or plant. They can be found in the gut of animals. When they get out of control – there is trouble.
- Pulpy kidney causes sudden death of calves after a change of feed – usually the biggest calf in the mob.
- Tetanus bacteria enter the body from a cut in the skin and lead to “lock jaw” and terminal seizures.
- Malignant oedema (gas gangrene) gets in from skin wounds, which become necrotic, then gassy – the animal then succumbs to blood poisoning.
- Black disease occurs secondarily to liver fluke infection. The immature liver fluke damage the liver, allowing clostridial bacteria to multiply, causing tissue damage followed by blood poisoning and death.
- Black leg causes necrosis and blackening of muscles (usually of the leg) followed by gas production, blood poisoning and death.
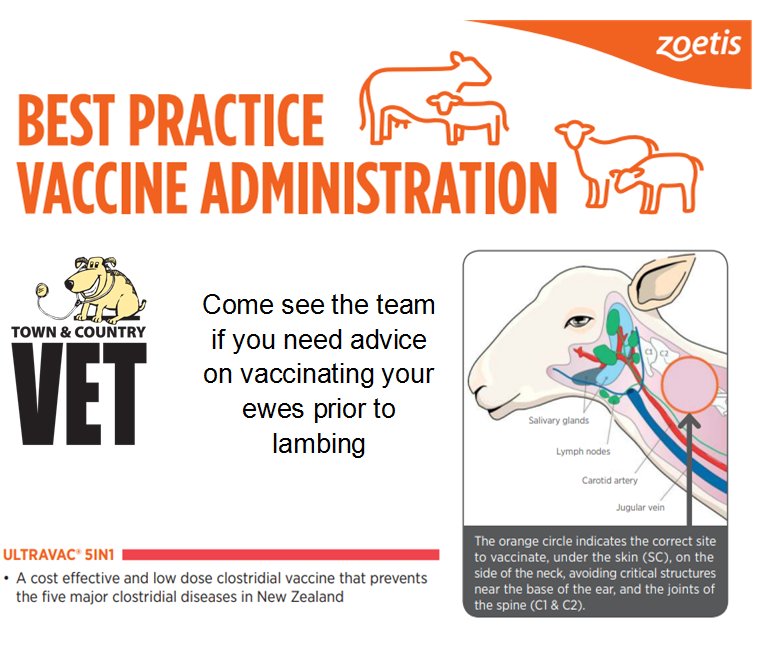
Traditionally these above diseases have been prevented by using “5 in 1” vaccines – e.g. Ultravac 5 in 1.
The normal vaccination protocol is a sensitizer dose of ‘eg. Ultravac 5 in 1’ , followed a month later by a booster dose.This can be given at any age for Ultravac but normally done at tailing.
To give immediate protection against tetanus at tailing, Lamb Vaccine can be given if you are not sure if the mother was correctly vaccinated which allows her to pass on protection to her lambs.
A booster dose is due every 12 months thereafter.